Your skin is itching and you’re wondering what’s causing it.
Both scabies and bed bugs can cause redness and itching on the skin. You can also get them both by sleeping on an infested bed.
So how do you know whether you’re dealing with scabies or bed bugs?
In this post, we’ll go over how these two pests are unique and how to treat them.
Let’s dive in!
What Are Scabies?
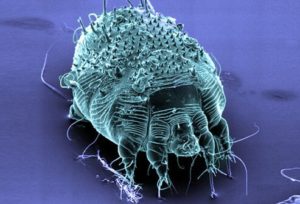
There are several types of Scabies that exist. The ones that are parasitic to humans are known as Sarcoptes Scabiei. These parasites infest and eat human skin.
Scabies infestation can be difficult to treat.
It is most common in crowded living conditions.
That’s because Sarcoptes Scabies is transmitted through direct contact. Transfer typically happens through skin, clothing, bedding, and towels.
What Are Bed Bugs?

Bed bugs are insects that require human blood to survive and breed. They commonly hide and live on their hosts bed but they will hide anywhere that their hosts sleeps frequently. This can range from couches to cars.
Infestations grow rapidly and they will continue to feed on the same host until they can expand to other hosts that are in close proximity.
They tend to bit in clusters of 2-3 until they have completed an entire blood meal. Their bites cause red, itchy welts that can have serious effects on people who experience continued bites.
These effects include rashes, allergic reactions, raspatory issues, and psychological effects such as sleep deprivation.
Scabies Vs. Bed Bugs: Appearance
The biggest difference between bed bugs and Scabies is size. Bed bugs are about 3/16th of an inch (4 to 5mm) while scabies is microscopic.
What Does Scabies Look Like?
Scabies are microscopic.
They have round bodies. They don’t have eyes or wings. They have eight legs.
What Do Bed Bugs Look Like?
Adult Bed bugs are about the size of short-grain, at around 3/16 on an inch (4 or 5mm).
They have six legs with two forward-facing and four backward facing legs. Their color range from light brown to dark brown.
Bed bugs have no hairs on the body.
Scabies Vs. Bed Bugs: Food
What Do Scabies eat?
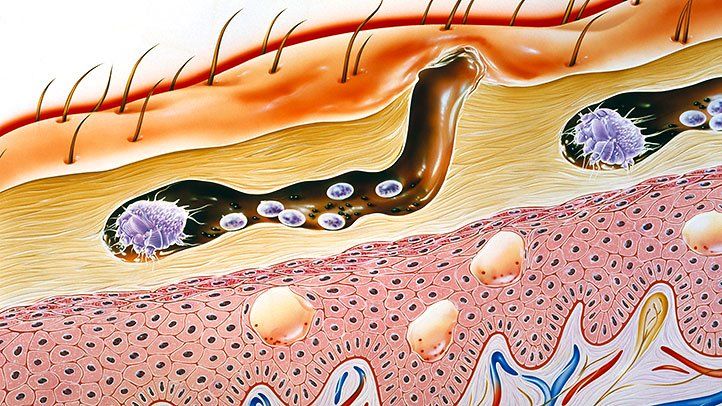
Scabies burrows underneath your skin to feed on the tissue and lay their eggs.
Bed bugs, on the other hand, drink human blood to survive.
What Do Bed Bugs Eat?

Bed bugs drink blood to survive.
They commonly feed on humans but will resort to warm-blooded mammals such as dogs, cats, birds, and rodents if humans are not around.
Scabies Vs. Bed Bugs: Habitat
Where Does Scabies Live?
Scabies mites burrow under the skin to lay eggs.
Females burrow using their mouthparts without direction. They eat the skin at around 0.5-5mm a day.
They can live anywhere in the body, but they are most common in:
- Between toes and fingers
- Wrist
- Elbow
- Knee folds
- Waistline
- Navel
- Armpits
Mite infestation to stabilize at a population of 15-20 females.
Where do bed bugs live?
Adult Bed bugs are about the size of short-grain, at around 3/16 on an inch (4 or 5mm).
They have six legs with two forward-facing and four backward facing legs. Their color range from light brown to dark brown.
Bed bugs have no hairs on the body.
Scabies Vs. Bed Bugs: Bites
Do Scabies Bite?
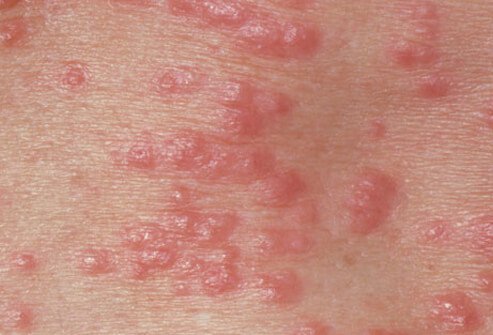
Yes. Scabies lives on and eats skin tissue. They tunnel into the skin at about .5-5mm a day.
These burrows typically look like raised grayish-white lines.
Common symptoms of Scabies bites include:
- Mild to severe itching
- scales
- bumps or blisters
- red patches
- raised, white rows
Symptoms of scabies generally take a few weeks to develop. During this time, infected persons may transfer the infection through direct contact.
Do Bed Bugs Bite?
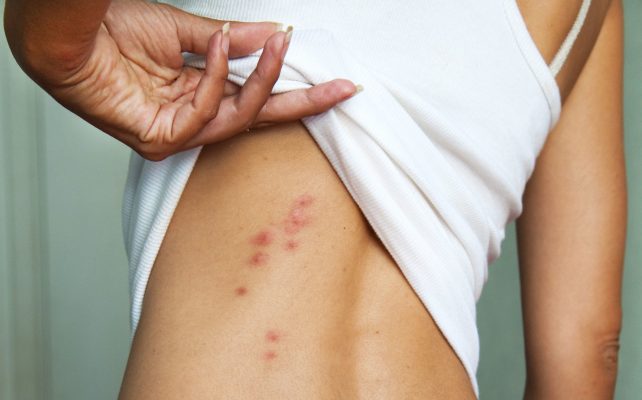

Yes. Bed bugs bite humans to feed on blood.
They also release an anesthetic to make their bites painless. Bed bugs also release anticoagulants so they can suck your blood as fast as possible.
Once bed bugs finished feeding, they return to their harborage until they are hungry again.
Bed bug bites look like welts and do not have a red spot at the center.
While the bites are not painful at first, they can eventually become swollen and irritated.
Bed bugs will bite you anywhere there is exposed skin.
Common locations for bed bites include:
- Arms
- Legs
- Ankles
- Back
- Torso
- Neck
- Feet
Scabies Vs. Bed Bugs: Dangers
Are Scabies Dangerous?
The main danger of scabies is skin irritation and infection.
Scabies can be extremely uncomfortable. Symptoms vary from mild to severe itching. Infected areas may also feel rough and crusty.
Scabies is also contagious and easily transmitted. You can transfer it through direct contact with skin, clothing, bedding, or towels.
It takes weeks for symptoms to be noticeable, so an infected person can easily transmit it unknowingly.
Are Bed Bugs Harmful?
Bed bugs do not carry any diseases and are relatively harmless compared to other pests.
That said, having a bed bug infestation can be disruptive.
Most people that have infestation suffer from itchiness.
Bed bug bites can cause excessive scratching that may lead to skin infections.
Their bites can be very uncomfortable, especially for young children.
People dealing with an infestation may also suffer from anxiety and lack of sleep.
Although rare, ned bug bites can cause allergic reactions that may need medical attention.
Finally, their bites can transmit parasites, although it’s not common.
Scabies Vs. Bed Bugs: Life Cycle
Scabies Life Cycle
Scabies life cycle happens in four stages: egg, larva, nymph, and adult.
Their entire life cycle happens in more or less two weeks.
After mating, females burrow their eggs in human skin. She will lay about two to three eggs every day.
Each egg is around .10 to .15 mm. The eggs will hatch within 48 hours.
The larva stays in small pockets of the human hair follicle for 3-4 days.
The larva will then molt into a nymph with four legs.
The last phase is the adult stage.
Females are about 0.30 to 0.45 mm long. Males are about half that size.
Females live to burrow and lay eggs for about one to two months.
Bed Bug Life Cycle
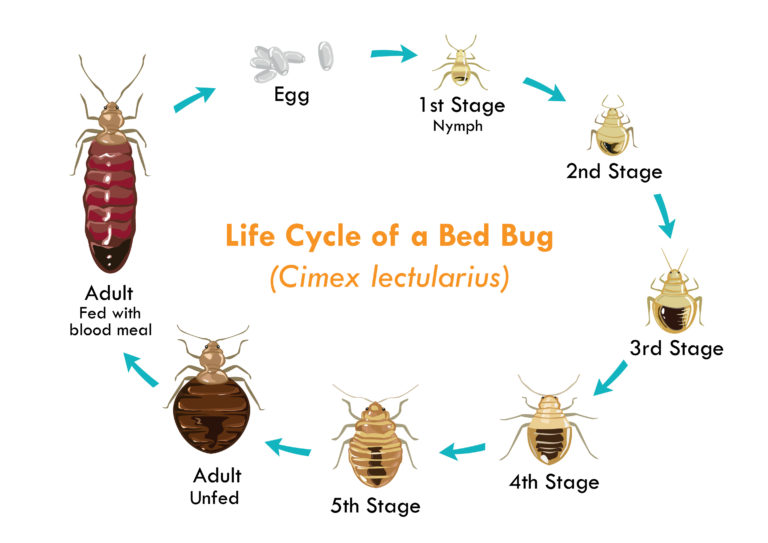
Bed bugs go through seven stages of development.
The first stage is the egg, followed by five different nymph stages and the adult stage.
During the nymph stages, bed bugs progressively grow larger.
Nymphs must eat at least once to reach the next phase of development.
Bed bugs eggs take around five to six weeks for bed bugs to reach adulthood.
Scabies Vs. Bed Bugs: Causes
What Causes Scabies?
Scabies gets transferred via direct, prolonged contact with the skin of an infected person. It may also be transferred through clothing, beddings, and towels.
Scabies outbreaks are most common in crowded areas such as nursing homes and prisons.
You may also get infected with scabies via sexual contact.
Scabies is seen worldwide and affects all people of all races.
What Causes Bed Bugs?
In most cases, bed bugs don’t invade your homes from the outdoors.
Bed bug typically hitchhikes their way into your home from another bed bug infested location.
These insects can travel though backpacks, luggage, clothes, grocery bags, etc. Bed bugs can also enter your home through used furniture, electronics, and clothing.
These bugs can hide inside used items for up to 12-14 months, even with the absence of food.
There are some reports of bed bugs walking across power lines and outdoor walls, but this is rare.
Scabies Vs. Bed Bugs: Treatment
How to get rid of Scabies?
Unlike what many believe, Scabies will not go away on their own.
The most common and effective way to get rid of Scabies in your skin is by using Scabicides.
Scabicides is a prescription medication dedicated to treating Scabies. You will not be able to get this over the counter.
Scabicides come in cream or lotion.
You’re typically required to leave the lotion on the infected skin for 8-14 hours before washing.
If you are infected with Scabies, it’s important to isolate yourself from direct human contact as much as possible to avoid spreading the infestation.
The treatment can last anywhere between a few days to a few weeks.
It’s also important to wash your clothes, bedding, and towels at high temperatures to avoid spreading Scabies. Wash the fabrics on high heat as well.
How To Get Rid of Bed Bugs?
There are several things you can do to eliminate bed bugs including:
- Washing, Steaming, and Vacuuming
- Heat Treatment
- Mattress Encasement
- Fumigation
- Bed Bug Traps
- Chemical Insecticide
The right method for you will depend on the severity of your infestation and your budget.
The following treatments are less expensive but more time-consuming:
- Washing, Steaming, and Vacuuming
- Mattress Encasement
- Bed Bug Traps
Keep in mind, these methods are only effective with careful application. It also typically takes longer to see results.
A more expensive option is to hire professional assistance. The methods professionals use include:
- Heat Treatment
- Fumigation
These treatment are either full home treatment or localized to sections of your home, depending or your needs.
While more costly, professional treatments are generally much faster and tend to produce results the same day or within several days.
Scabies Vs. Bed Bugs: Prevention
How To Prevent Scabies?
The only way to prevent scabies is to prevent direct, prolonged contact with the infected person.
You’ll also want to avoid any fabrics that have come in contact with their skin. Stay away from their beddings, towels, and clothing.
If your family member has scabies, get the proper treatment. Wash all their clothes, bedding, and towels with hot water.
How To Prevent bed Bugs?
Preventing bed bug requires active monitoring. Since these pest tend to hitchhike their way into your house you need to monitor at all time.
One of the best ways to prevent bed bugs is to monitor any furniture or used items you are bringing into your home.
The key is to look for the signs of bed bugs on any new or current furniture.
Common signs of bed bugs include:
- Skin Irritation
- Brown Stains
- Bloodstains
- Dead Bed Bugs
- Musty Smell
- Red Bumps Or Welts / Bed Bug Bites
- Nymphs or Eggs
- Adult Bed Bugs
- Discarded Shells
