There are three main types of termites found in the US: Subterranean, Drywood, and Dampwood.
Under these main types are dozens of termite species subtypes. Each one is unique in their biology, behavior, and economic impact.
Here we’ll go over the different types of termites species and their impact on households.
1. Subterranean Termites
Subterranean termites make about 90% of termite damage in the US each year.
Their colonies are the largest of any insects in the US, reaching up to a million members each.
They start new colonies after two to six years of being established. And they can increase to several hundred thousand in 6 to 7 years.
Subterranean termites live in soil, but will enter homes to feed on anything that has cellulose including the foundation, walls, roof, etc.
They easily penetrate wood that’s in direct contact with the ground.
If the wood does not contact the soil, Subterranean termites will build mud tubes to access wood above the ground.
These tunnels allow them to travel safely between the food source and the nest.
Because they live in soil, Subterranean termites are some of the most challenging pests to identify and treat.
They eat both soft and dry wood and are much less picky eaters than their termite cousins.
Appearance:
Subterranean termites have a long, narrow, white body that’s about 1/8 inch long.
Their head can be light orange to dark brown. They have 6 legs and 2 straight antennas.
Types of Subterranean Termites
There are many species of Subterranean termites. Most live in the desert and are not household pests..
The two species of Subterranean termites that are notorious pests in the US are the Formosan and Eastern Subterranean.
Here’s a list of the different types of Subterranean termites:
- Formosan
- All Across the U.S with heavy concentration in coastal states.
- Eastern Subterranean
- All Across the U.S, except Alaska.
- Desert Subterranean
- Texas, California, Arizona, New Mexico, and Nevada
- Arid Land Subterranean
- Located across the entire U.S except the East. Popular in the South West, Pacific Coast, and Mid West.
- Dark Southeastern Subterranean
- Located in the Eastern United States, typically from Florida up to New England.
- Western Subterranean
- California, Nevada, Oregon, Washington, Idaho, and Arizona
- West Indian Subterranean
- Found across the globe in South America, India, Asia,and in some cases tropical climates in the U.S such as Florida.
2. Eastern Subterranean Termites
Eastern Subterranean Termites is a type of Subterranean termite.
They are in every state in the US except Alaska. And they are the most destructive termites in California.
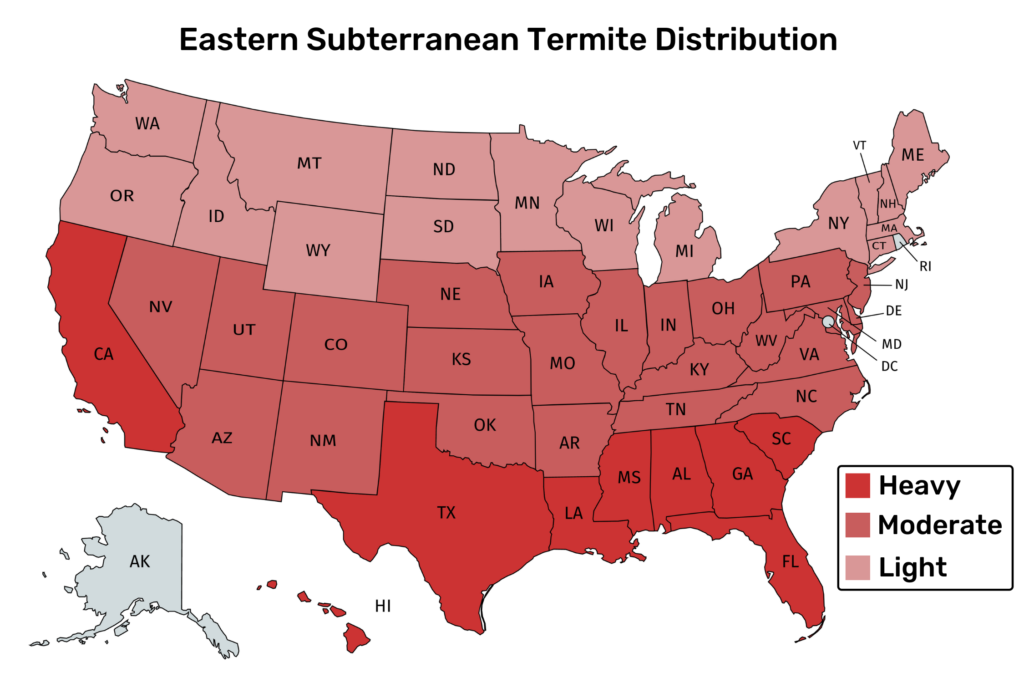
A mature Eastern Subterranean colony can contain hundreds of thousands of termites.
They live and feed underground. But these termites will enter your home to access food.
You’ll often see them live in walls, basements, and crawl spaces.
Appearance:
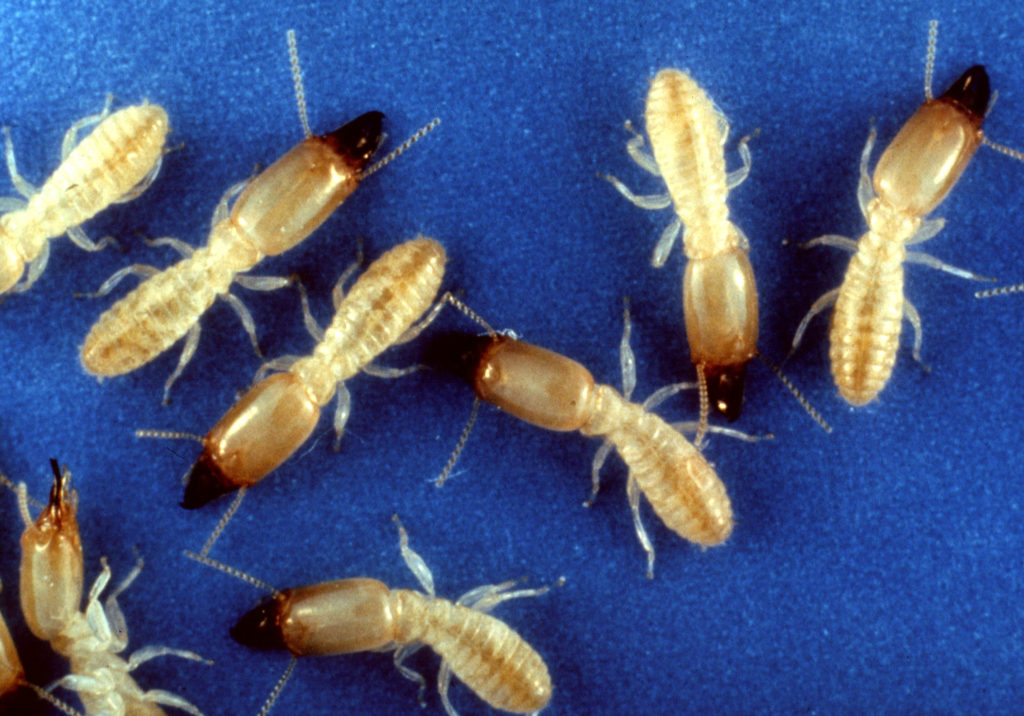

Within Eastern subterranean termite colonies are three castes: workers, soldiers, and reproductives.
Their workers are white or cream-colored and feed on wood.
Soldiers have large mandibles with light-colored bodies.
Reproductives, known as alates, have wings and are dark brown.
3. Formosan Termites
Formosan Termites are a type of Subterranean termite.
You can find them across the US.
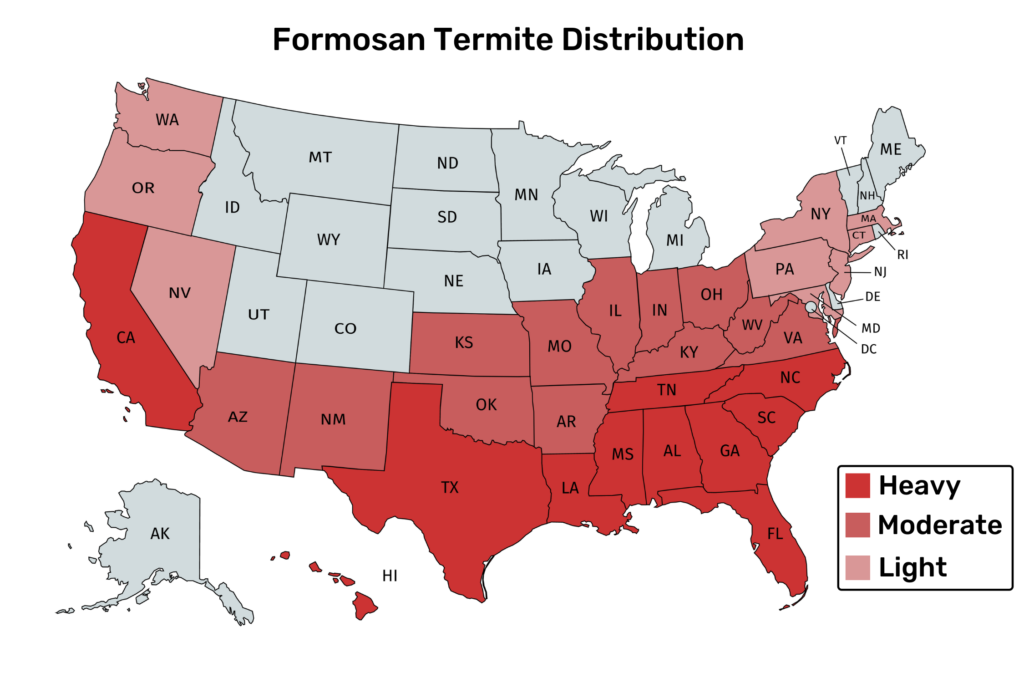
But they are more concentrated in southern states including South Carolina, Mississippi, Georgia, Florida, Alabama, Louisiana and Tennessee.
Formosan termites are known to make a secondary nest, called carton nests, with saliva, wood, and excrement.
These nests allow them to maintain a moist environment above ground.
If you have a Formosan termite infestation, you’ll likely find these “carton” nests inside your walls.
Appearance:
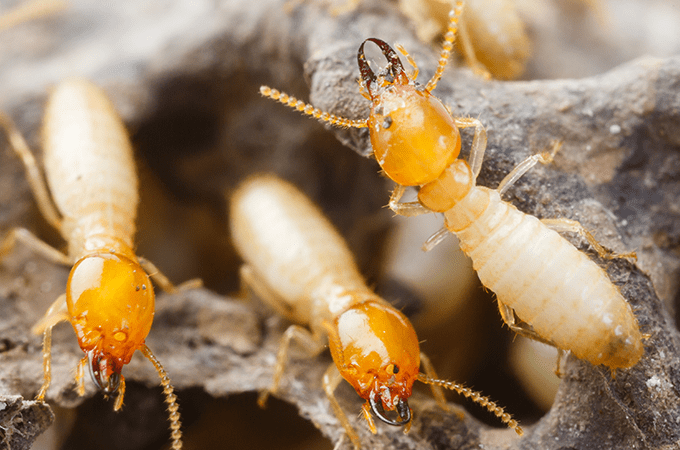

Within Formosan termite colonies are three castes: workers, soldiers, and reproductives.
The reproductives, known as Alates, are about 14-15mm in length if you include their wings.
They have pale yellow to brownish-yellow bodies and translucent wings.
Formosan termite workers have creamy, white bodies and dark brown heads with two sharp pincers.
Their soldiers have oval-shaped heads with large mandibles.
4. Drywood Termites
Drywood termites belong to the family Kalotermitidae.
The majority of them in the US are in a narrow coastal strip from Florida to California.
Unlike subterranean termites, drywood termites do not require contact with soil.
They nest in wood, such as dead trees, walls, or wooden floors and furniture.
Drywood termite colonies are much smaller than subterranean.
A mature Drywood termite colony has about 4,000 termites and expand between two to three colonies per home.
That said, Drywood termite infestation shouldn’t be taken lightly.
These pests spread their colonies in different parts of your home. That means mature drywood termite colonies can cause significant damage to multiple parts of your home simultaneously.
Drywood termites produce small, dry droppings called pellets or frass.
Drywood termite pellets look a lot like sand or sawdust.
But unlike sand, a drywood pellet has six concave surfaces.
They are hard, elongated, and less than 1/25 inch long.
Drywood frass can be different colors, depending on the color of the wood termites have been eating.
You may find traces of pellets into their feeding tunnel.
In most cases, Drywood termites use “kick out” holes to remove pellets from their tunnels.
Appearance:
Drywood termites grow at around 3/8 to 2/3 of an inch.
They vary in appearance, depending on their role within the colony.
Workers have white bodies with dark heads.
Soldier termites range from cream to brown with large mandibles for fighting other insects.
Reproductives, known as Alates, are brown to black.
Types of Drywood Termites
There are many species of Drywood termites. The most common Drywood termite in the US is the Western Drywood termite.
Here are the diffent types Drywood Termites:
- Western Drywood
- All Coastal States – From Florida to California sometimes found in Oregon and Washington.
- Southeastern Drywood
- South Carolina to Florida and west to Texas. Widely distributed in the southeast U.S
- Desert Drywood
- Arizona and California
5. Western Drywood Termite
The western drywood termites are the most common drywood termite in the U.S.
It is most abundant in the southwestern United States but also found in the southeastern states such as Florida, Georgia, Alabama, Tennesse, North Carolina, and South Carolina.
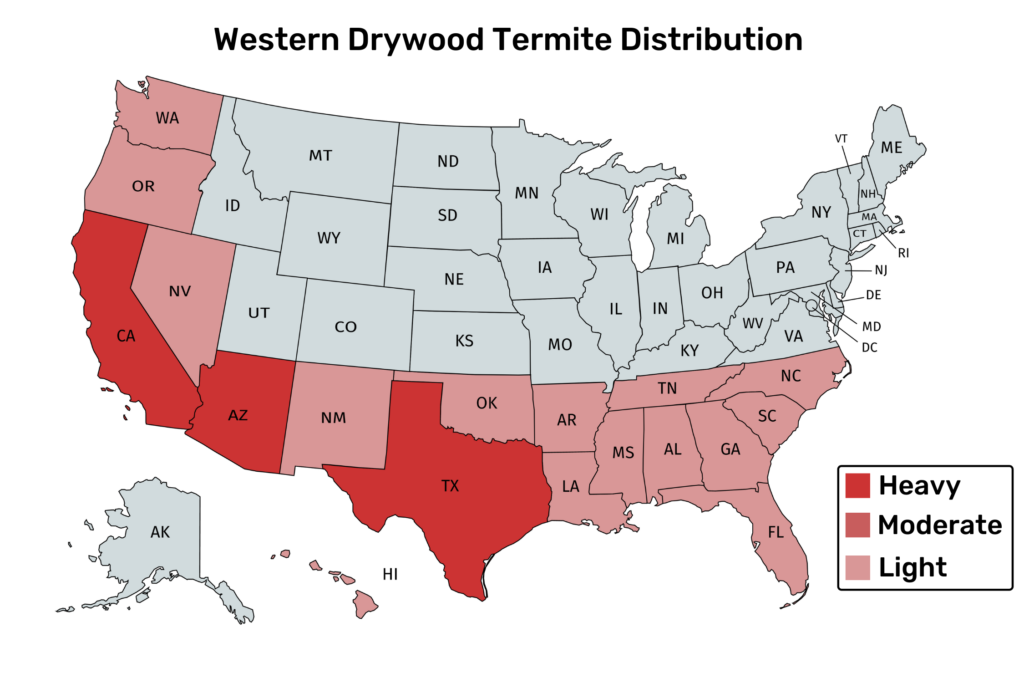
These termites don’t require contact with the soil and live primarily in dry, sound wood in human-made structures.
A common sign of western drywood termites is their droppings and kick-out holes.
They often go unnoticed for years since they live deep inside the wood, and their populations tend to grow much slower than Subterranean termites.
Appearance:
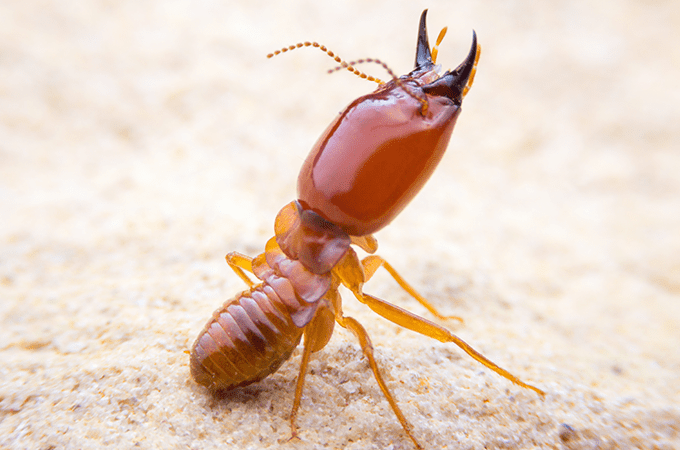

Western Drywood termites are typically on the lighter side when compared to other termites.
Soldiers have a tan body and orange head.
They are also known for their large mandibles that tend to be black or dark brown.
Alates are typically brown with tan or white wings.
6. Dampwood Termites
Dampwood Termites live in wood with high moisture content.
As such, they are known to infest damp and rotting wood.
You’ll generally find them fence posts sheds, eaves decks, porch, and outdoor furniture.
Dampwood termites are abundant in the Pacific Coast states, including Northern California, Oregon, and Washington State.
You can also find them in Florida, Hawaii, Nevada, Idaho, and Montana.
Unlike drywood termites, dampwood termites do not expel their pellets into “kick out” holes.
Instead, they use their droppings to seal their home from the outside world.
These pellets look like soft concrete plastered on damaged wood.
They are typically easy to spot because the coverage is imperfect.
Another characteristic of Dampwood termites that are different from other termites is that they don’t have workers.
Instead, they have the nymphs, known as Pseudergates, to do the job typically done by termite workers.
Like termite workers, Pseudergates forage for food, take care of the young, and build nests.
The nymphs can grow into reproductives later if needed.
Appearance:
Dampwood termites can grow up to ¾” long. They are the largest of all termites species in North America.
They have colors ranging from yellowish-brown to cinnamon-brown.
They also have a flat brown head and long dark brown to black mandibles.
Their Reproductives, also known as Alates, are dark brown with brown wings.
Types of Dampwood Termites
Of all the species of Dampwood termites, the Nevada and the Pacific Dampwood do the most damage to homes.
In contrast, the Florida Dampwood rarely infests homes and does the least amount of economic damage.
Here are the diffent types Dampwood Termites:
- Nevada Dampwood
- Nevada, Idaho, and Montana
- Pacific Dampwood
- California, Oregon, and Washington, all coastal states, Nevada, Montana, Idaho, Southwest U.S, and Florida
- Desert Dampwood
- Texas, Arizona, New Mexico, and California
- Florida Dampwood
- South Florida and the Florida Keys
7. Pacific Dampwood
Pacific Dampwood termites are the largest of the Dampwood species.
They are found on the Pacific Coast of the United States, such as California, Nevada, Idaho, Montanna, Oregon, and Washington.
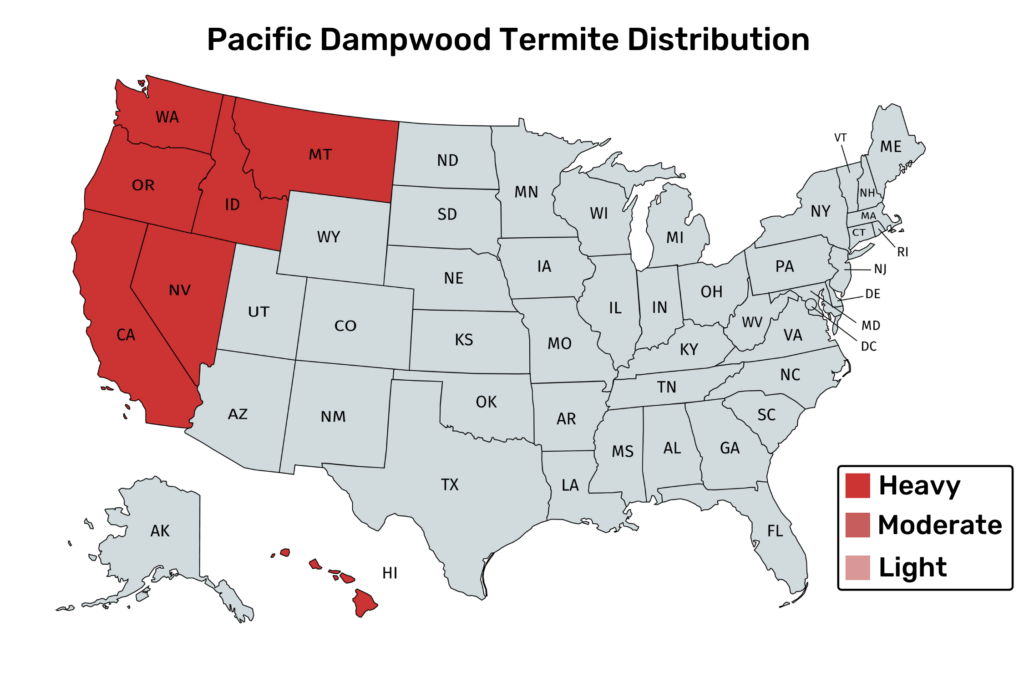
Along the coast, these termites are common in piers, boathouses, docks, beach houses.
Pacific Dampwood termites require the moisture from wet or damp wood.
This is why they prefer to live in decaying or water damaged wood.
Appearance:
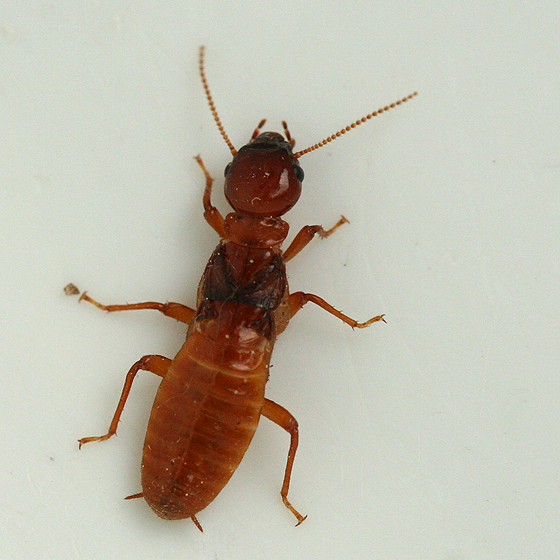

Soldiers have large flattened heads with large mandibles.
They typically have a yellow or light brown body and a brown head.
Nymphs are white or cream-colored.
Alates are dark brown or black with brown wings.
8. Conehead Termites
“Conehead Termites” are named after their cone-like heads.
They are native to the Caribbean, Central America, South America, and the West Indies.
This species of termites was first introduced to the United States in the early 2000s.
And the only state in the US that has them is Florida.
They build their nest above ground. You’ll typically find them on tree trunks, base, and branches.
Conehead termites’ nests look similar to a big ball of dirt.
But their nests are composed of feces, wood, and dirt.
Mature Conehead termites can reach several hundred thousand to a million.
Conehead Termites eat both dry and softwood.
These pests will infest homes and eat any wood they find walls, furniture, walls, fence posts, etc.
They will also consume dead trees and grass.
What’s fascinating about this termite species are their soldiers.
Soldiers make up about 20% of the colony.
But, unlike other termites, its the Conehead soldiers that locate food items for the colony.
Once they find food, they recruit workers to harvest them.
Appearance:
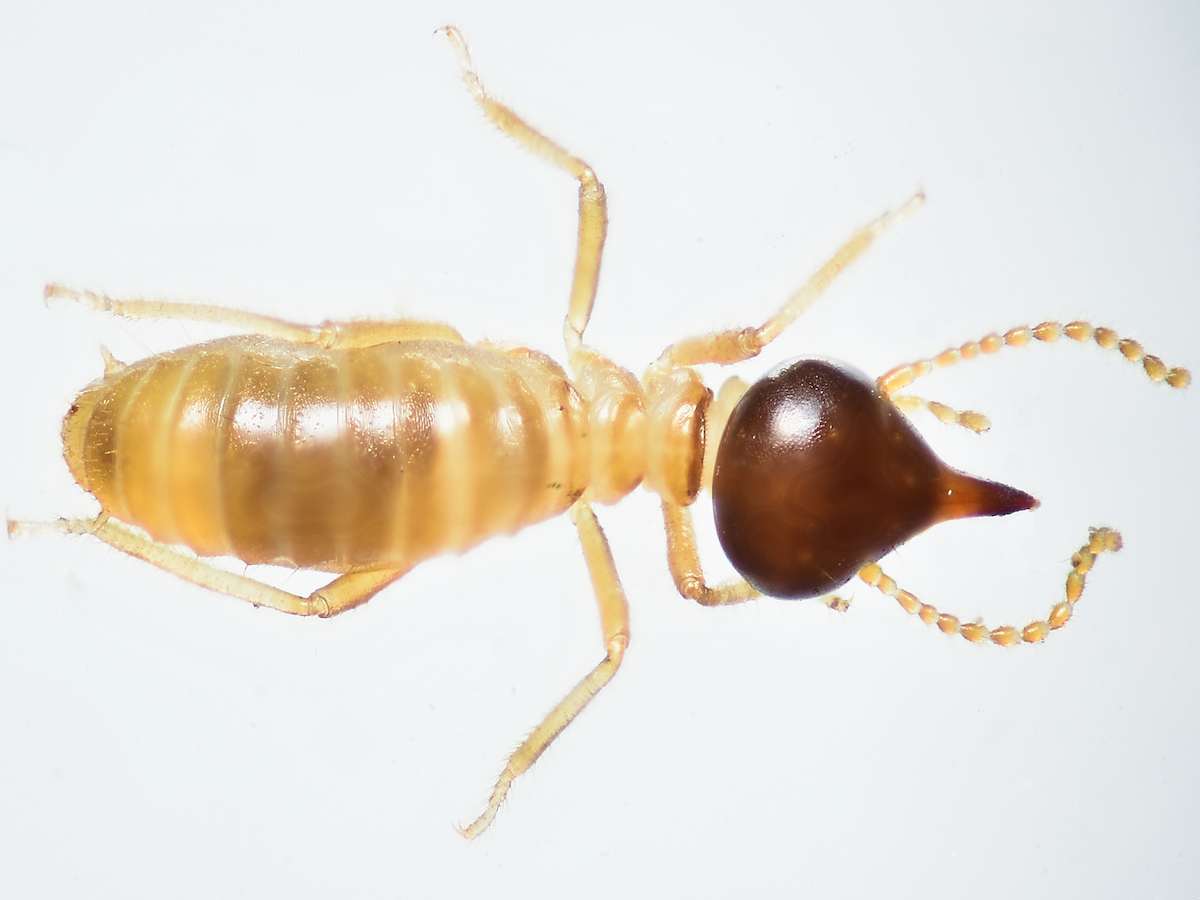

Conehead termites have a dark brown cone-shaped head and cream-colored bodies.
Worker and soldier termites are tiny, growing only up to about 3-4mm in length.
Reproductives or Alates are fairly large at about 15 mm.
9. Macrotermes
Macrotermes, also known as mound building termites, are found primarily in Africa and Asia.
They are considered more advanced than other termite species.
Macrotermes have evolved to cultivate wood into a much richer food source by turning it nto fungus.
To do this, they eat and swallow the wood.
Then they return to their nest, where they remove the materials as pseudofeces.
The pseudofeces are then cultivated into fungus.
Macrotermes are also considered advanced because they can build mounds that reach up to 30 feet tall.
If humans are the size of termites, the structure will be about 3.5 miles tall. Something we haven’t been able to accomplish.
Another unique characteristic of this species of termite is their soldiers emit a corrosive liquid when attacking or defending the colony.
Appearance:
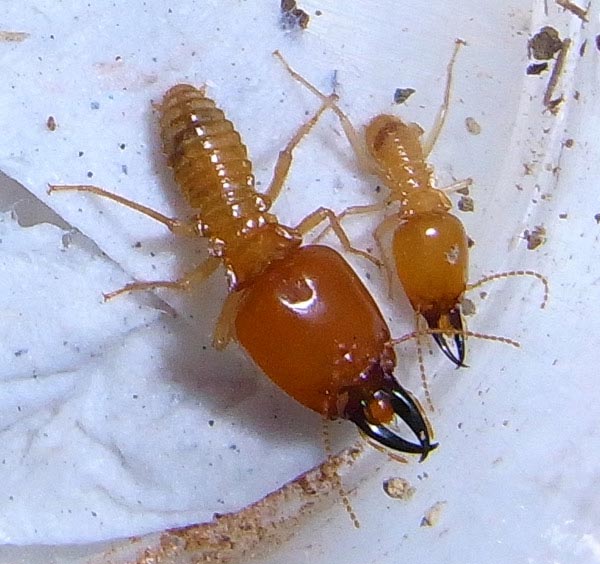

Macroteremes have two sizes of workers and soldiers.
They are split between major and minor workers.
These termites look very similar to that of a drywood termite.
Soldiers have a white or pale brown abdomen with a darker head and large mandibles.
Major soldiers are similar in size to drywood termites, with the exception that their heads are wider.
While most, take on the light brown and orange color, one species is black.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
How to Treat Subterranean Termites?
Subterranean termites can easily access any wood that is in direct contact with soil.
So, the first step to eliminating these pests in your home is to remove all wood-to-soil contact.
Make sure to keep wood sidings, fences, decks, doors, and window framing above ground level.
Posts and stairs planted in concrete are also susceptible to rotting and termite infestation.
Removing wood-to-soil contact for these may require removing soil back from the foundation and cutting the bottom off the wood.
You can also use a barrier, such as a waterproof substance, between the wood and the soil.
I also recommend using pressure-treated wood, particularly in posts and stairs, for added protection.
Another step you can take to treat Subterranean termites is to use chemical barriers.
To do this, you can spray the soil beneath the foundation with insecticides.
You can also drill holes through the foundation and inject insecticides beneath the foundation.
Finally, you can use Termite traps to control the population of Subterranean termites.
Termite traps, a.k.a Termite Stakes, are bait stations designed to eliminate termites.
These stations do not trap termites. Instead, they entice termites to ingest deadly chemicals using bait.
The bait can be anything with cellulose, such as wood and paper.
Termite traps are useful because they are slow-acting.
When worker termites eat them, they don’t die right away.
Instead, they return the food to the nest and spread the bait to the entire colony.
Since other members rely on worker termites for food, you only need a few soldiers to feed on the bait to kill a significant population.
How to Treat Drywood Termites?
There are two types of treatment you can take Drywood termite infestation: Whole Structure and Localized treatment.
Whole Structure treatments are best for houses with larger infestations.
It implements the simultaneous treatment of all infestation in a structure.
Localized or spot treatment is applied to more targeted areas and works best for smaller infestations.
Localized Treatment
Localized or spot treatment is applied to targeted areas.
The idea is to identify where the colony is located correctly.
Once located, the treatment is applied directly onto the termites.
For this treatment to be effective, you’ll need to detect precisely where the termites are.
The four types of localized treatments that are proven to be effective are:
Wood Replacement
As the name suggests, wood replacement involves replacing the infested wood.
Wood replacement is ideal if the infestation is only on a few pieces of wood.
After replacing the wood, I recommend you treat the new wood to prevent the termites from coming back.
You can do this by applying a layer of termiticide or bora-care to all sides of the area of the new wood.
Localized Dust / Foam Treatment
Localized Dust or Foam Treatment involves injecting pesticides into the infested wood.
These pesticides can come in the form of liquid, dust, or foam formulations.
Using dust is more effective than foam unless there’s moisture in the wood. Foam is also a better option for larger wall voids.
To apply either dust or foam treatment, drill into the wood and inject the termite galleries with pesticides.
Liquid Nitrogen – Cold Treatment
Cold treatment involves injecting liquid nitrogen into infested areas.
The downside of this method is you’ll likely need professional help, which can be costly.
That said, this approach is free of toxic chemicals.
Heat – Localized Thermal Treatment
Localized heat treatment involves heating infested wood above 120°F, which is fatal to termites.
Heat treatment is an excellent option if you’re looking to treat your home without using chemicals.
Similar to cold treatment, heat treatments require hiring professionals, which can be expensive.
Whole Structure
Whole Structure treatment requires that you hire a professional pest control agency.
This method is best if you suspect you have a significant infestation.
The two types of whole structure treatment are: fumigation and heat.
Fumigation
Fumigation is the process of releasing a fumigant in your home to kill termites.
To do this, professionals must first place a tent over your home.
Fumigation is an excellent solution for large termite infestation.
Studies show that it can eliminate 97% of termites after application.
Heat
Heat treatment uses propane heaters to raise temperature to levels that are deadly to termites.
It’s one of the most effective ways to eradicate termite infestation.
The California Department of Consumer Affairs has even gone on to say that heat is the only sufficient, full-structure treatment for eliminating termite.
And in this study, the heat method was also proven to kill 99% of termites consistently.
Resource: The Best Ways To Get Rid of Drywood Termites
How to treat Dampwood termites?
The same methods treat Dampwood termites as drywood termites: Whole Structure and Localized treatment.
To prevent Damp wood termites, make sure to eliminate excess moisture from your home.
Look for any leaky plumbing and make sure to get them repaired.
Make sure to eliminate damaged and rotting wood in your property.
Keep your rain gutters, downspouts, and splash blocks are functioning correctly. They should keep the water at least five feet minimum from your foundation wall.
Keep any dripping water from your air conditioning away from your foundation.
You can also keep moisture away by using moisture meters.
Moisture meters read the moisture level in your home.
This way, you’ll know if your moisture levels might lead to termite infestation.
The standard acceptable moisture levels for exterior wood in most states range from 9% to 14%.
Any moisture reading above that range is likely too much and could attract termites.
What are the three types of termites?
The three main types of termites are Subterranean, Dampwood, and Drywood termites.
Two main differences between these three species of termites are where they live and what they eat.
Subterranean Termites live underground. They need moisture and contact with soil to survive.
Dampwood Termites live deep inside damp and rotting wood. They need moisture to survive.
Drywood termites live deep inside of wood. They can eat dry wood and don’t need as much moisture to survive.
What is the worst type of termite?
Subterranean Termites are the worst termites to get in your home.
They make about 90% of termite damage in the U.S. each year.
There are a few reasons for this.
The first is that they build large colonies that can reach up to a million members.
Second, they live in the soil, making them invulnerable to many termite treatments.
Subterranean Termites are also ferocious eaters. They eat both soft and dry wood.
What do termites look like to the human eye?
While termites are small, they are visible with the human eye.
They are comparable in size to most household ants.
Winged termites, or Alates, are generally larger and are much easier to identify.
Unlike other termites, Alates also go out in the open to mate. As such, they are typically the first sign of infestation homeowners recognize.
How common are termites in California?
Termites are pretty common in California.
That’s primarily because the state has moderate weather and high-humidity.
Termites are cold-blooded and thrive in warm weather. They also need moisture to survive.
As such, Califonia is an ideal location for termites to live.
That’s true for Subterranean, Dampwood and Drywood termites.
Will termites die in the sun?
Termites will die if they are exposed to the sun for too long.
Termites need moisture to survive. So, leaving them exposed in the sun will cause them to dehydrate and die.
That said, they can survive several minutes of direct sunlight.
Drywood termites can last the longest in the sun since it doesn’t need as much moisture as its termite cousins.
Do termites have to return to the ground?
Subterranean termites live in soil and are the only termite species that have to return to the ground.
Drywood and Dampwood termites live inside wood and don’t require direct contact with the soil.
What are the types of termites in California?
California is home to Drywood, Subterranean, and Dampwood termites.
The warm weather, high humidity, and abundance of water due make California an ideal location for termites.
Why do I have termites in my bedroom?
Termites can and will infest any part of your house for as long as there is cellulose.
Materials that have cellulose include wood walls, fabric, books, cardboard, and wooden furniture.
For most houses, you can find cellulose in every room.
The only other reason you’ll see a termite in your room other than cellulose is a swarm.
Swarming is an event where flying termites, known as Alates, leave their nest to mate.
Alates are the only termites that come out in the open and are attracted to light.
Flying termite were likely drawn to your room by a light source.
If you see a flying termite, that means that there is a termite infestation nearby, and it is expanding.
As such, you must take immediate action.
How do I know what kinds of termites I have?
The easiest way to identify what termite you have is to observe their behavior.
Drywood Termites
If you see kick out holes and pallets around your home, you have a drywood infestation.
Drywood termite pellets look a lot like sand or sawdust.
But unlike sand, a drywood pellet has six concave surfaces.
They are hard, elongated, and less than 1/25 inch long.
Drywood frass can be different colors, depending on the color of the wood termites have been eating.
You’ll find pallets next to kick out holes. Drywood termites use “kick out” holes to remove pellets from their tunnels. (See image below).
Subterranean Termites
If you see mud tubes, you have a Subterranean Termites infestation.
Mud tubes help Subterranean termites to travel safely
between a food source and the nest.
You’ll typically find these tubes on or near the soil.
You may find them near your pipes, in your attic, crawlspace, or along your foundation.
Mud tubes typically take on three forms: working tube, exploratory tube, and drop tube.
Working tube and Exploratory tube look like veins running up against your wall.
Drop tubes look like calcium deposits that hang in caves. Except they hang from the ceiling.
Dampwood Termites
Unlike drywood termites, Dampwood termites do not expel their pellets into “kick out” holes.
Instead, they use their droppings to seal their home from the outside world.
These pellets look like soft concrete plastered on damaged wood.
They are typically easy to spot because the coverage is imperfect.
Can you hear termites In your walls?
Termites are noisy eaters.
Sometimes you’ll be able to hear them eating if you place your ear against your walls.
You can also knock on your walls and listen for quiet clicking sounds.
Soldier termites produce this sound when disturbed. They bang their heads or shake their bodies to warn the rest of the colonies.
Resource: Top 13 Signs You Have Termites
